What is a Cover Board
How a cover board can help you mitigate risks.
This video tells you what can happen without a cover board in your roofing system.Why use a cover board?
A cover board is a rigid component in a low-slope roofing system used to enhance durability and resiliency. Its key function is to protect your roof from damage.A glass-mat gypsum cover board can help your roof stand up to fire, wind uplift, hail and punctures.
Where does it go?
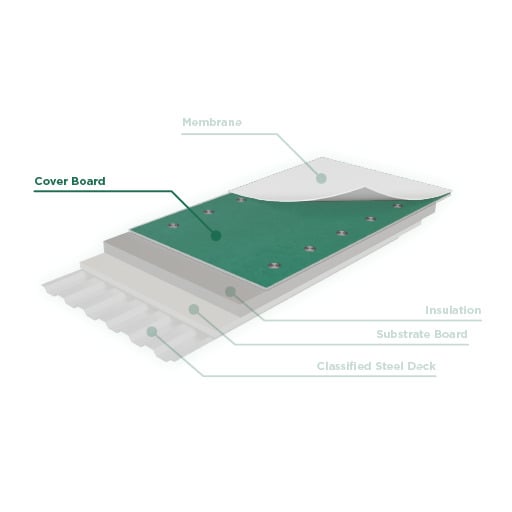
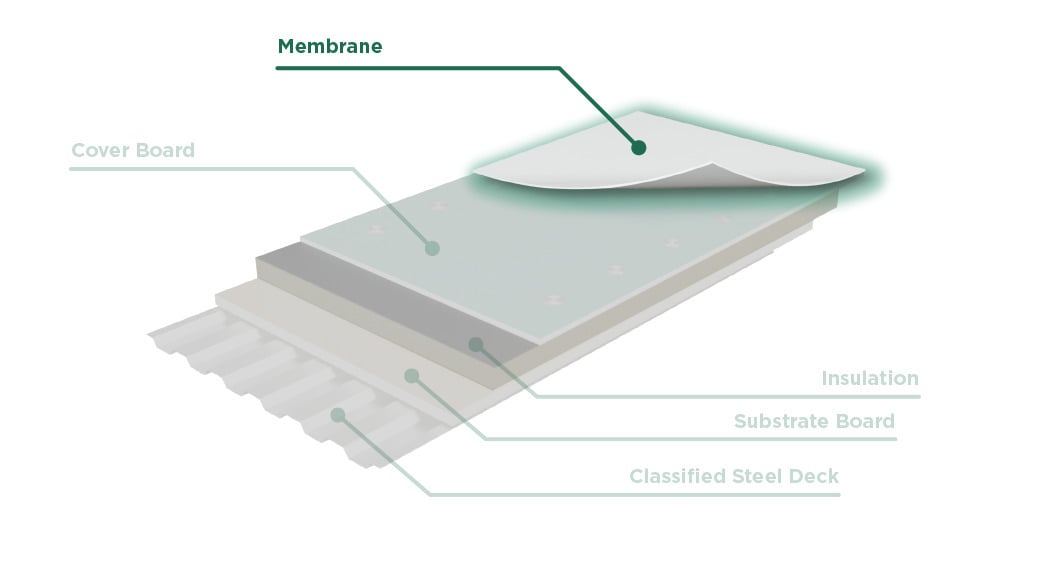
A cover board is typically installed below the waterproofing membrane and above the insulation.
Glass-mat gypsum cover board can also be installed in the “roof board position” at the bottom of the roofing assembly. Here, it would protect the roof from internal fire within the building. This could help prevent the roofing system from becoming additional fuel.
Cover board options and comparison
Did you know that system manufacturers require a cover board for a 30-year roof? That’s why several types are available. See the differences in your options below.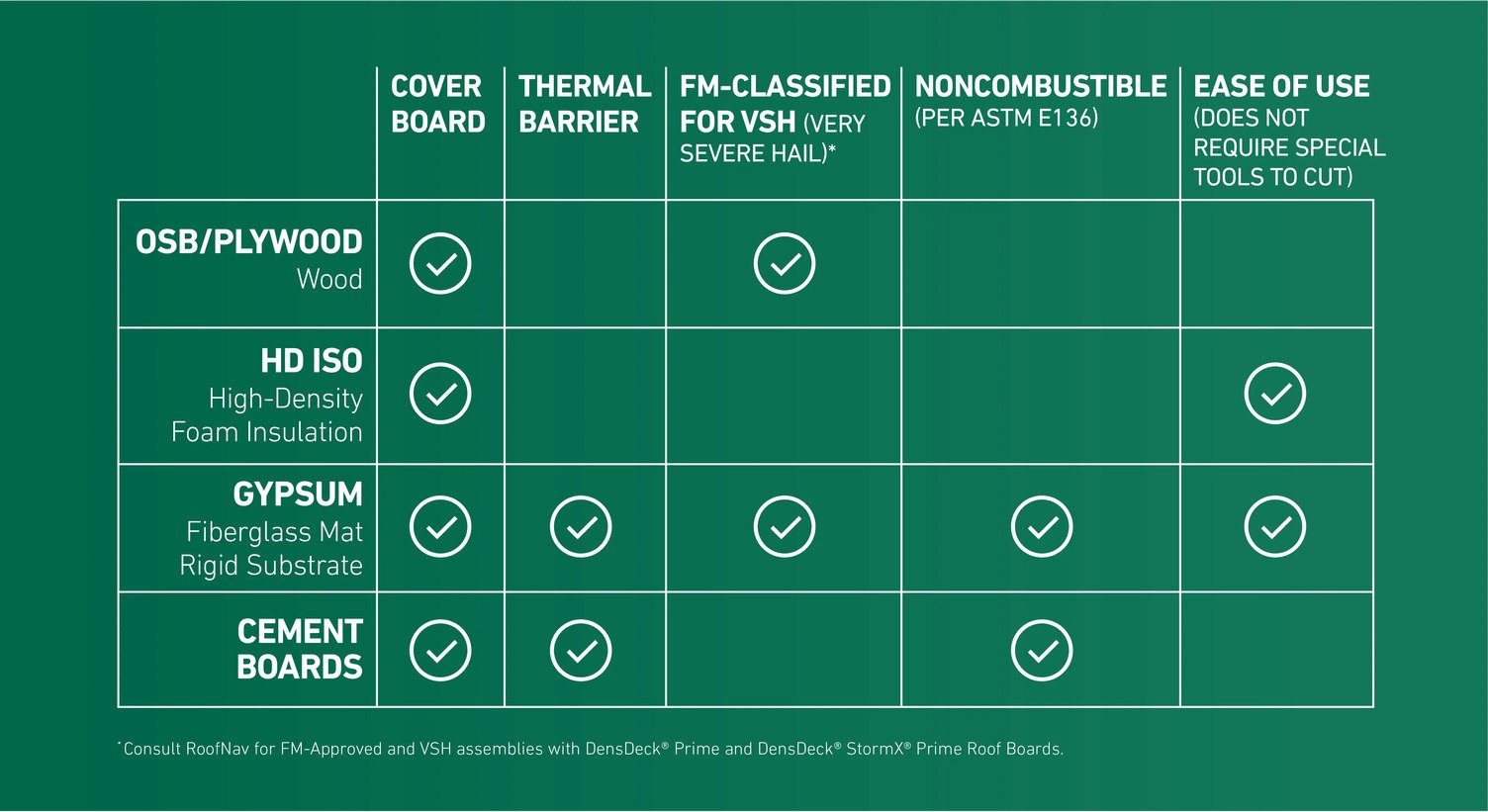
Common membrane choices
A roof that can stand up to high winds, heavy rain and severe hail starts with a strong, durable membrane.
EPDM – (Ethylene Propylene Diene Terpolymer)
A resilient, synthetic elastomer. Available in black and white, in a variety of widths and two thicknesses, 45 and 60-mil. It can be installed either fully adhered, mechanically attached or ballasted, with seams sealed by liquid adhesives or specially formulated tape.
TPO – (Thermoplastic Polyolefin)
A reflective, white roofing material made primarily from recycled rubber. Can be fastened, attached or ballasted. Must be installed in dry conditions due to the heat adhesion seaming process. Material quality varies drastically among manufacturers, which may cause price variability.
PVC – (Polyvinyl Chloride)
A durable, long-lasting, reflective, white plastic monomer. Flexible and resistant to moisture, wind, fire and chemicals. Available in a range of widths and thicknesses from 50 to 80-mil.
MOD Bit – (Modified Bitumen)
A durable, flexible material made of asphalt combined with either polymerized rubber (SBS—styrene-butadiene-styrene) or plasticized polymers (APP—atactic polypropylene). It is then reinforced with fiberglass to create a waterproof membrane. Usually installed from rolls directly onto the substrate via an adhesive. The material may be heat-welded, cold-adhered, or in some cases, self-adhered or mechanically attached.
All it takes is a single ember
Building owners probably aren’t thinking about roof damage before installation. But you can make sure they’re prepared for the worst.Whether it’s from a neighboring building or faulty electrical wiring, commercial building fires can escalate quickly. Using noncombustible roofing materials like gypsum can help mitigate the spread of fires that cause damage, injury and loss of life.
Discover How to Prepare Your Roof with a gypsum cover board to help you mitigate risks.

SOURCE:
1 Nonresident Fire Estimate Summaries – Nonresident building fire trends (2013-2022). U.S. Fire Administration (page last reviewed Dec. 2024). https://www.usfa.fema.gov/statistics/nonresidential-fires/

